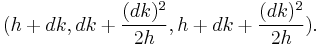Formulas for generating Pythagorean triples
Besides Euclid's formula, many other formulas for generating Pythagorean triples have been developed.
Euclid's, Pythagoras', and Plato's formulas
Euclid's , Pythagoras' and Plato's formulas for calculating triples have been described here:
The methods below appear in various sources, often without attribution as to their origin.
Some variations on Euclid's method
A trivial sequence that generates some but not all possible triples is based on the positive integers starting with a = 3.
- If a is odd, then b = a2/2 − 1/2 and c = b + 1
- If a is even, then b = a2/4 − 1 and c = b + 2
Note that a = 3 and a = 4 produce the same primitive triple and that when a = 4n + 2 for integer n (thus a is even), then the triple produced is non-primitive and simply the corresponding primitive from the odd sequence with all values doubled.
More formally: given a positive integer n, the triple can be generated by the following two procedures: (see http://www.mcs.surrey.ac.uk/Personal/R.Knott/Pythag/pythag.html )
Example: When n = 2, the triple produced is 5, 12, and 13. (This formula is actually the same as method I, substituting m with 2n + 1.)
Alternatively, one can generate triples from even integers using the following formulas. Given that m is an positive even number,
Example: When m = 4 the triple produced is 8, 15, and 17 (This formula is another specific case of method I, substituting n with 1).
These two methods generally produce different results, but when n is 1 in the first formula and m is 2 in the second formula, the result is 3, 4, 5. This method yields Pythagorean triples (not all of them primitive) for any given value, under the conditions given, but it does not yield all valid Pythagorean triples, or even all primitive Pythagorean triples. The pattern that the odd values express is visible in the scatter plot of triples as the darker radiating lines. The even sequence is present, but harder to see. The smallest primitive triple based on values for c that this sequence does not find is (20, 21, 29) whose multiples appear as a pair of lighter radiating lines near the diagonal of the scatter plot.
Given the integers u and v, (see: http://www.math.rutgers.edu/~erowland/pythagoreantriples.html )
Example: For u = 3 and v = 5, a = 39, b = 80, c = 89. (This formula is actually the same as method I, substituting m and n with u + v and v.)
For the resulting triple to be primitive, u and v must be co-prime and u must be odd.
A particularly elegant version of this method is to calculate
Then
Fibonacci's method
Leonardo of Pisa (c. 1170 – c. 1250) described this method[1][2] for generating primitive triples using the sequence of consecutive odd integers 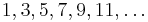 , and the fact that the sum of the first
, and the fact that the sum of the first  terms of this sequence is
terms of this sequence is 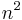 . If
. If 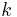 is the
is the  -th member of this sequence then
-th member of this sequence then 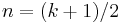 .
.
Choose any odd square number 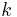 from this sequence (
from this sequence (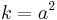 ) and let this square be the
) and let this square be the  -th term of the sequence. Also, let
-th term of the sequence. Also, let 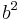 be the sum of the previous
be the sum of the previous 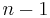 terms, and let
terms, and let 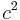 be the sum all
be the sum all  terms . Then we have established that
terms . Then we have established that 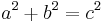 and we have generated the primitive triple [ a, b, c]. This method produces an infinite number of primitive triples, but not all of them.
and we have generated the primitive triple [ a, b, c]. This method produces an infinite number of primitive triples, but not all of them.
EXAMPLE: Choose 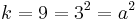 . This odd square number is the fifth term of the sequence [because
. This odd square number is the fifth term of the sequence [because 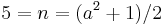 ]. The sum of the previous 4 terms is
]. The sum of the previous 4 terms is 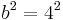 and the sum of all
and the sum of all 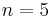 terms is
terms is 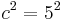 giving us
giving us 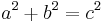 and the primitive triple [ a, b, c] = [ 3, 4, 5].
and the primitive triple [ a, b, c] = [ 3, 4, 5].
Progressions of whole and fractional numbers
The German monk and mathematician Michael Stifel published the following method in 1544.[3][4]
Consider the progression of whole and fractional numbers: 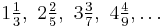
The properties of this progression are: (a) the whole numbers are those of the common series and have unity as their common difference; (b) the numerators of the fractions, annexed to the whole numbers, are also the natural numbers; (c) the denominators of the fractions are the odd numbers, 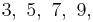 etc.
etc.
To calculate a Pythagorean triple: select any term of this progression and reduce it to an improper fraction. For example, take the term 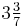 . The improper fraction is
. The improper fraction is 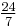 . The numbers 7 and 24 are the sides, a and b, of a right triangle, and the hypotenuse is one greater than the largest side. For example:
. The numbers 7 and 24 are the sides, a and b, of a right triangle, and the hypotenuse is one greater than the largest side. For example:
Jacques Ozanam[5] republished Stifel’s sequence in 1694 and added the similar sequence 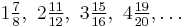 with terms derived from
with terms derived from 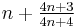 . The hypotenuse of the triple(s) produced is 2 greater than the larger side. For example:
. The hypotenuse of the triple(s) produced is 2 greater than the larger side. For example:
Dickson's method
L. E. Dickson (1920)[6] attributes to himself the following method for generating Pythagorean triples. To find integer solutions to 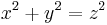 , find positive integers r, s, and t such that
, find positive integers r, s, and t such that 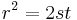 is a square.
is a square.
Then:
From this we see that 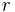 is any even integer and that s and t are factors of
is any even integer and that s and t are factors of 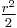 . All Pythagorean triples may be found by this method. When s and t are coprime the triple will be primitive.
. All Pythagorean triples may be found by this method. When s and t are coprime the triple will be primitive.
Example: Choose r = 6. Then 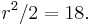 The three factor-pairs of 18 are: (1, 18), (2, 9), and (3, 6). All three factor pairs will produce triples using the above equations.
The three factor-pairs of 18 are: (1, 18), (2, 9), and (3, 6). All three factor pairs will produce triples using the above equations.
- s = 1, t = 18 produces the triple x = 6 + 1 = 7, y = 6 + 18 = 24, z = 6 + 1 + 18 = 25.
- s = 2, t = 9 produces the triple x = 6 + 2 = 8, y = 6 + 9 = 15, z = 6 + 2 + 9 = 17.
- s = 3, t = 6 produces the triple x = 6 + 3 = 9, y = 6 + 6 = 12, z = 6 + 3 + 6 = 15. Since s and t are not coprime, this triple is not primitive.
Generalized Fibonacci sequence
I.
For Fibonacci numbers starting with F1=0 and F2=1 and with each succeeding Fibonacci number being the sum of the preceding two, one can generate a sequence of Pythagorean triples starting from (a3, b3, c3) = (4, 3, 5) via
for n ≥ 4. See also Fibonacci triangles.
II.
A Pythagorean triple can be generated using any two positive integers by the following procedures using generalized Fibonacci sequences.
For initial positive integers hn andhn+1, if hn+hn+1=hn+2 and hn+1+hn+2=hn+3, then
is a Pythagorean triple.[7]
III.
The following is a matrix-based approach to generating primitive triples with generalized Fibonacci sequences.[8] Start with a 2 × 2 array and insert two coprime positive integers ( q,q' ) in the top row. Place the even integer (if any) in the left-hand column.
Now apply the following "Fibonacci rule" to get the entries in the bottom row:
Such an array may be called a "Fibonacci Box". Note that q', q, p, p' is a generalized Fibonacci sequence. Taking column, row, and diagonal products we obtain the sides of triangle [a, b, c], its area A, and its perimeter P, as well as the radii ri of its incircle and three excircles as follows:
The half-angle tangents at the acute angles are q/p and q'/p'.
EXAMPLE:
Using coprime integers 9 and 2.
The column, row, and diagonal products are: (columns: 22 and 117), (rows: 18 and 143), (diagonals: 26 and 99), so
The half-angle tangents at the acute angles are 2/11 and 9/13. Note that if the chosen integers q, q' are not coprime, the same procedure leads to a non-primitive triple.
Pythagorean triples and Descartes' circle equation
This method of generating primitive Pythagorean triples also provides integer solutions to Descartes' Circle Equation,[8]
where integer curvatures ki are obtained by multiplying the reciprocal of each radius by the area A. The result is k1 = pp', k2 = qp', k3 = q'p, k4 = qq'. Here, the largest circle is taken as having negative curvature with respect to the other three. The largest circle (curvature k4) may also be replaced by a smaller circle with positive curvature ( k0 = 4pp' − qq' ). EXAMPLE: Using the area and four radii obtained above for primitive triple [44, 117, 125] we obtain the following integer solutions to Descartes' Equation: k1 = 143, k2 = 99, k3 = 26, k4 = (−18), and k0 = 554.
A Ternary Tree: Generating All Primitive Pythagorean Triples
Each primitive Pythagorean triple corresponds uniquely to a Fibonacci Box. Conversely, each Fibonacci Box corresponds to a unique and primitive Pythagorean triple. In this section we shall use the Fibonacci Box in place of the primitive triple it represents. An infinite ternary tree containing all primitive Pythagorean triples/Fibonacci Boxes can be constructed by the following procedure.[9]
Consider a Fibonacci Box containing two, odd, coprime integers x and y in the right-hand column.
It may be seen that these integers can also be placed as follows:
resulting in three more valid Fibonacci boxes containing x and y. We may think of the first Box as the “parent” of the next three. For example, if x = 1 and y = 3 we have:
Moreover, each "child" is itself the parent of three more children which can be obtained by the same procedure. Continuing this process at each node leads to an infinite ternary tree containing all possible Fibonacci Boxes, or equivalently, to a ternary tree containing all possible primitive triples. (The tree shown here is distinct from the classic tree described by Berggren in 1934, and has many different number-theoretic properties.) Compare: "Classic Tree".[10] See also Tree of primitive Pythagorean triples.
Generating triples using a square
Start with any square number  . Express that number in the form
. Express that number in the form 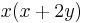 ; then
; then 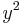 will produce another square such that
will produce another square such that 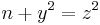 . For instance:
. For instance:
Let 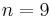 ; then
; then 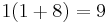 ,
, 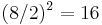 , and
, and 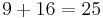 .
.
Let 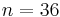 ; then
; then 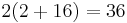 ,
, 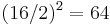 , and
, and 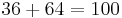 .
.
This works because 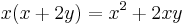 . If we add
. If we add 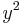 , our expression becomes
, our expression becomes 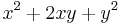 , which factors into the form
, which factors into the form 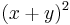 .[11]
.[11]
Generating triples when one side is known
(This method is a direct algebraic manipulation of the Euclid equations).
Start with any integer 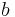 . Use this relation from the Euclid formula:
. Use this relation from the Euclid formula: 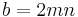 . If
. If 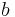 is odd, then multiply
is odd, then multiply 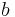 by 2. Identify all factor-pairs (m,n) of
by 2. Identify all factor-pairs (m,n) of 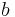 and use the Euclid equations to calculate the remaining sides of the triple.
and use the Euclid equations to calculate the remaining sides of the triple.
Examples: Let 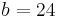 (e.g. the known side is even)
(e.g. the known side is even)
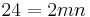 so that
so that 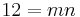 . The factor pairs (m,n) of 12 are (12,1), (6,2) and (4,3). The three possible triples are therefore:
. The factor pairs (m,n) of 12 are (12,1), (6,2) and (4,3). The three possible triples are therefore:
Let 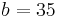 (e.g. the known side is odd)
(e.g. the known side is odd)
The two unknown sides could also be calculated by making use of the relation 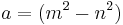 . This would be a factoring exercise in finding the difference of two squares, but a simpler approach is to divide the known side by two and continue as before:
. This would be a factoring exercise in finding the difference of two squares, but a simpler approach is to divide the known side by two and continue as before:
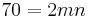 so that
so that 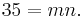
The factor pairs (m,n) of 35 are (35,1), (7,5).
The two triples are therefore (note that is necessary to remove the factor of 2 which was introduced):
Generating triples using quadratic equations
There are several methods for defining quadratic equations for calculating each leg of a Pythagorean triple[12]. A simple method is to modify the standard Euclid equation by adding a variable x to each m and n pair. The m, n pair is treated as a constant while the value of x is varied to produce a “family” of triples based on the selected triple. An arbitrary coefficient can be placed in front of the “x” value on either m or n, which causes the resulting equation to systematically “skip” through the triples. For example, let’s use the triple [20, 21, 29] which can be calculated from the Euclid equations with a value of m = 5 and n = 2. Also, let’s arbitrarily put the coefficient of 4 in front of the “x” in the “m” term.
Let 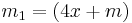 and let
and let 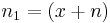
Hence, substituting the values of m and n:
Note that the original triple comprises the constant term in each of the respective quadratic equations. Below is a sample output from these equations. Note that the effect of these equations is to cause the “m” value in the Euclid equations to increment in steps of 4, while the “n” value increments by 1.
x side a side b side c m n
0 20 21 29 5 2
1 54 72 90 9 3
2 104 153 185 13 4
3 170 264 314 17 5
4 252 405 477 21 6
Pythagorean triples by use of matrices and linear transformations
Let ![[\text{ }a,\text{ }b,\text{ }c]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/cf709cffa930de29aeacef2be4f52699.png) be a primitive triple with
be a primitive triple with 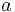 odd. Then 3 new triples
odd. Then 3 new triples ![[{{a}_{1}},{{b}_{1}},{{c}_{1}}], \text{ }[{{a}_{2}},{{b}_{2}},{{c}_{2}}], \text{ }[{{a}_{3}},{{b}_{3}},{{c}_{3}}]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/f1260a9a80f4a23ff4702669959adbbd.png) may be produced from
may be produced from ![[\text{ }a,\text{ }b,\text{ }c]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/cf709cffa930de29aeacef2be4f52699.png) using matrix multiplication and Berggren’s[10] three matrices A, B, C. Triple
using matrix multiplication and Berggren’s[10] three matrices A, B, C. Triple ![[\text{ }a,\text{ }b,\text{ }c]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/cf709cffa930de29aeacef2be4f52699.png) is termed the "parent" of the three new triples (the "children"). Each child is itself the parent of 3 more children, and so on. If one begins with primitive triple
is termed the "parent" of the three new triples (the "children"). Each child is itself the parent of 3 more children, and so on. If one begins with primitive triple ![[\text{ }3,\text{ }4,\text{ }5]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/66519f47ee8f419d922eafc04db2e63c.png) , all primitive triples will eventually be produced by application of these matrices. The result can be graphically represented as an infinite ternary tree with
, all primitive triples will eventually be produced by application of these matrices. The result can be graphically represented as an infinite ternary tree with ![[\text{ }a,\text{ }b,\text{ }c]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/cf709cffa930de29aeacef2be4f52699.png) at the root node. An equivalent result may be obtained using Berggrens's three linear transformations shown below.
at the root node. An equivalent result may be obtained using Berggrens's three linear transformations shown below.
Berggren's three linear transformations are:
Alternatively, one may also use 3 different matrices found by Price.[9] These matrices A', B', C' and their corresponding linear transformations are shown below.
Price's three linear transformations are:
The "3 children" produced by each of the two sets of matrices are not the same, but each set separately produces all primitive triples.
EXAMPLE: Using [ 5, 12, 13] as the parent, we get two sets of three children:
Area proportional to sums of squares
All primitive triples with 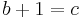 and with a odd can be generated as follows:[13]
and with a odd can be generated as follows:[13]
| Pythagorean triple | Semi-perimeter | Area | Incircle radius | Circumcircle radius |
|---|---|---|---|---|
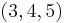 |
1 + 2 + 3 | 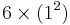 |
1 | 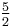 |
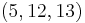 |
1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 | 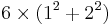 |
2 | 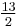 |
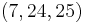 |
1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 | 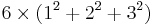 |
3 | 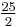 |
| ....... | ....... | ....... | ....... | ....... |
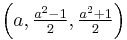 |
1 + 2 + ... + a | ![6\times \left[ 1^2%2B2^2%2B\cdots%2B\left( \tfrac{a-1}{2} \right)^2 \right]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/3936a23f2eb381314bd6c749521aaf58.png) |
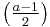 |
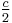 |
Height-excess enumeration theorem
Wade and Wade[14] first introduced the categorization of Pythagorean triples by their height, defined as c - b, linking 3,4,5 to 5,12,13 and 7,24,25 and so on.
McCullough and Wade[15] extended this approach, which produces all Pythagorean triples when 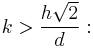 Write a positive integer h as pq2 with p square-free and q positive. Set d = 2pq if p is odd, or d= pq if p is even. For all pairs (h,k) of positive integers, the triples are given by
Write a positive integer h as pq2 with p square-free and q positive. Set d = 2pq if p is odd, or d= pq if p is even. For all pairs (h,k) of positive integers, the triples are given by
The primitive triples occur when gcd(k, h) = 1 and either h=q2 with q odd or h=2q2.
References
- ^ Fibonacci, Leonardo Pisano, (1225), Liber Quadratorum.
- ^ Fibonacci, Leonardo Pisano . The Book of Squares (Liber Quadratorum). An annotated translation into modern English by L. E. Sigler. (1987) Orlando, FL: Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-643130-8
- ^ Stifel, Michael, (1544), Arithmetica Integra.
- ^ Ozanam, Jacques (1814). Recreations in Mathematics and Natural Philosophy. 1. G. Kearsley. p. 49. http://books.google.com/?id=s_IJAAAAMAAJ&pg=RA3-PA49&lpg=RA3-PA49&dq=%22progression+of+whole+and+fractional+numbers%22&q=%22progression%20of%20whole%20and%20fractional%20numbers%22. Retrieved 2009-11-19.
- ^ Ozanam, Jacques, (1844). Science and Natural Philosophy: Dr. Hutton’s Translation of Montucla’s edition of Ozanam, revised by Edward Riddle, Thomas Tegg, London. Read online- Cornell University
- ^ Dickson, Prof L. E., (1920), History of the Theory of Numbers, Vol.II. Diophantine Analysis, Carnegie Institution of Washington, Publication No. 256, 12+803pp Read online - University of Toronto
- ^ Horadam, A. F., "Fibonacci number triples", American Mathematical Monthly 68, 1961, 751-753.
- ^ a b Bernhart, Frank R. and Price, H. Lee; Lee Price (2005). "Heron's formula, Descartes circles, and Pythagorean triangles". arXiv:math/0701624v1 [math.MG].
- ^ a b Price, H. Lee (2008). "The Pythagorean Tree: A New Species". arXiv:0809.4324 [math.HO].
- ^ a b Berggren, B. (1934). "Pytagoreiska trianglar" (in Swedish). Tidskrift för elementär matematik, fysik och kemi 17: 129–139.
- ^ Sloane's A129861 . The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. OEIS Foundation.
- ^ J. L. Poet and D. L. Vestal, Jr. (2005). “Curious Consequences of a Miscopied Quadratic, ” College Mathematics Journal 36 , 273–277.
- ^ Barbeau, Edward, Power Play, Mathematical Association of America,1997, p. 51, item 3.
- ^ Wade, Peter, and Wade, William, "Recursions that produce Pythoagorean triples", College Mathematics Journal 31, March 2000, 98-101.
- ^ McCullough, Darryl, and Wade, Elizabeth, "Recursive enumeration of Pythagorean triples", College Mathematics Journal 34, March 2003, 107-111.
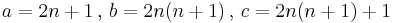
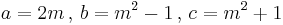
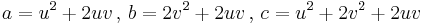
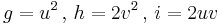
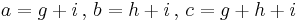
![1\tfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\xrightarrow{\text{yields}}\text{ }[3,4,5],\text{ 2}\tfrac{2}{5}\text{ }\xrightarrow{\text{yields}}\text{ }[5,12,13],\text{ 3}\tfrac{3}{7}\text{ }\xrightarrow{\text{yields}}\text{ }[7,24,25],\text{ 4}\tfrac{4}{9}\text{ }\xrightarrow{\text{yields}}\text{ }[9,40,41],\text{ }\ldots](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/8b1648c654d2a6f5b93e15ff364b7492.png)
![1\tfrac{7}{8}\xrightarrow{\text{yields}}[8,15,17],2\tfrac{11}{12}\xrightarrow{\text{yields}}[12,35,37],3\tfrac{15}{16}\xrightarrow{\text{yields}}[16,63,65],4\tfrac{19}{20}\xrightarrow{\text{yields}}[20,99,101],\ldots](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/075b1febd5611777d98fbfb190555d3c.png)
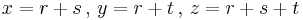
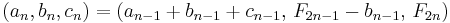
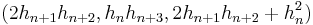
![\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}c}
q & {q'} \\
\bullet & \bullet
\end{array}} \right]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/aace151827589c22bfea5a2757be71c9.png)
![\begin{array}{*{20}c}
q' %2B q = p \\
q %2B p = p'
\end{array} \to \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}c}
q & q' \\
p & p'
\end{array}} \right]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/09b83e1df0bd8d1c89b2bbde768f9241.png)
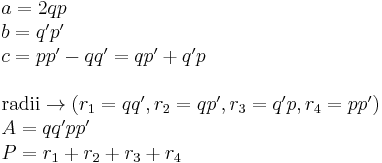
![\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}c}
2 & 9 \\
\bullet & \bullet
\end{array}} \right] \to \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}c}
2 & 9 \\
11 & 13
\end{array}} \right]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/1a829b50970173e2cb29e93b27d72939.png)
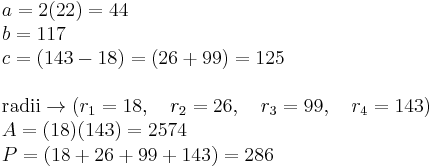
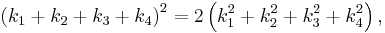
![\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
\bullet & x \\
\bullet & y
\end{array}} \right]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/b64bfa7764a18b70110b6447a109c027.png)
![\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
\bullet & x \\
y & \bullet
\end{array}} \right],\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
x & y \\
\bullet & \bullet
\end{array}} \right],\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
y & x \\
\bullet & \bullet
\end{array}} \right]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/c0ba97aa1403609dbeedcdd9539f0af0.png)
![\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
1 & 1 \\
2 & 3
\end{array}} \right] \leftarrow \text{parent}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/1631680171e6b8d1fd40f39023c99d5b.png)
![\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
2 & 1 \\
3 & 5
\end{array}} \right],\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
1 & 3 \\
4 & 5
\end{array}} \right],\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
3 & 1 \\
4 & 7
\end{array}} \right] \leftarrow \text{children}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/8681df3b2729a3be9a57f204b8c364bb.png)
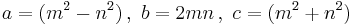
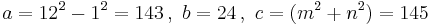
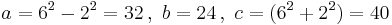
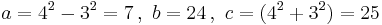
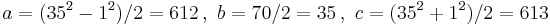
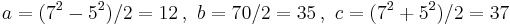
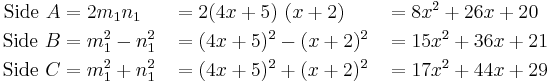
![\overset{A}{\mathop{\left[ \begin{matrix}
-1 & 2 & 2 \\
-2 & 1 & 2 \\
-2 & 2 & 3 \\
\end{matrix} \right]}} \left[ \begin{matrix}
a \\
b \\
c \\
\end{matrix} \right]=\left[ \begin{matrix}
a_1 \\
b_1 \\
c_1 \\
\end{matrix} \right],\quad \text{ }\overset{B}{\mathop{\left[ \begin{matrix}
1 & 2 & 2 \\
2 & 1 & 2 \\
2 & 2 & 3 \\
\end{matrix} \right]}} \left[ \begin{matrix}
a \\
b \\
c \\
\end{matrix} \right]=\left[ \begin{matrix}
a_2 \\
b_2 \\
c_2
\end{matrix} \right],\quad \text{ }\overset{C}{\mathop{\left[ \begin{matrix}
1 & -2 & 2 \\
2 & -1 & 2 \\
2 & -2 & 3
\end{matrix} \right]}} \left[ \begin{matrix}
a \\
b \\
c
\end{matrix} \right]=\left[ \begin{matrix}
a_3 \\
b_3 \\
c_3
\end{matrix} \right]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/26d47b63755a55bdcc3854a39778ecd7.png)
![\begin{align}
& \begin{matrix}
-a%2B2b%2B2c=a_1 \quad & -2a%2Bb%2B2c=b_1 \quad & -2a%2B2b%2B3c=c_1 & \quad\to \left[ \text{ }a_1,\text{ }b_1,\text{ }c_1 \right] \\
\end{matrix} \\
& \begin{matrix}
%2Ba%2B2b%2B2c={{a}_{2}} \quad & %2B2a%2Bb%2B2c={{b}_{2}} \quad & %2B2a%2B2b%2B3c={{c}_{2}} & \quad\to \left[ \text{ }{{a}_{2}},\text{ }{{b}_{2}},\text{ }{{c}_{2}} \right] \\
\end{matrix} \\
& \begin{matrix}
%2Ba-2b%2B2c={{a}_{3}} \quad & %2B2a-b%2B2c={{b}_{3}} \quad & %2B2a-2b%2B3c={{c}_{3}} & \quad\to \left[ \text{ }{{a}_{3}},\text{ }{{b}_{3}},\text{ }{{c}_{3}}\right] \\
\end{matrix} \\
&
\end{align}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/eacb1abe8f6bae5363edb9c0f9ed1b34.png)
![\overset{{{A}'}}{\mathop{\left[ \begin{matrix}
2 & 1 & -1 \\
-2 & 2 & 2 \\
-2 & 1 & 3
\end{matrix} \right]}} \left[ \begin{matrix}
a \\
b \\
c
\end{matrix} \right]=\left[ \begin{matrix}
a_1 \\
b_1 \\
c_1
\end{matrix} \right],\quad \text{ }\overset{{{B}'}}{\mathop{\left[ \begin{matrix}
2 & 1 & 1 \\
2 & -2 & 2 \\
2 & -1 & 3
\end{matrix} \right]}} \left[ \begin{matrix}
a \\
b \\
c \\
\end{matrix} \right]=\left[ \begin{matrix}
a_2 \\
b_2 \\
c_2
\end{matrix} \right],\quad \text{ }\overset{{{C}'}}{\mathop{\left[ \begin{matrix}
2 & -1 & 1 \\
2 & 2 & 2 \\
2 & 1 & 3 \\
\end{matrix} \right]}} \left[ \begin{matrix}
a \\
b \\
c \\
\end{matrix} \right]=\left[ \begin{matrix}
a_3 \\
b_3 \\
c_3
\end{matrix} \right]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/3561719ff379e79d48623611d9ba324e.png)
![\begin{align}
& \begin{matrix}
%2B2a%2Bb-c=a_1 \quad & -2a%2B2b%2B2c=b_1 \quad & -2a%2Bb%2B3c=c_1 & \quad \to \left[ \text{ }a_1,\text{ }b_1,\text{ }c_1 \right]
\end{matrix} \\
& \begin{matrix}
%2B2a%2Bb%2Bc=a_2 \quad & %2B2a-2b%2B2c=b_2 \quad & %2B2a-b%2B3c=c_2 & \quad \to \left[ \text{ }a_2,\text{ }b_2,\text{ }c_2 \right]
\end{matrix} \\
& \begin{matrix}
%2B2a-b%2Bc=a_3 \quad & %2B2a%2B2b%2B2c=b_3 \quad & %2B2a%2Bb%2B3c=c_3 & \quad \to \left[ \text{ }a_3,\text{ }b_3,\text{ }c_3 \right]
\end{matrix} \\
&
\end{align}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/cde3e8062f7aab0212dba6edca830f39.png)
![\begin{matrix}
{} & \left[ \text{5},12,13 \right] & {} \\
A & B & C \\
\left[ 45,28,53 \right] & \left[ \text{55,48,73} \right] & \left[ \text{7,24,25} \right]
\end{matrix}\quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \begin{matrix}
{} & \left[ \text{5},12,13 \right] & {} \\
{{A}'} & {{B}'} & {{C}'} \\
\left[ 9,40,41 \right] & \left[ \text{35,12,37} \right] & \left[ \text{11,60,61} \right]
\end{matrix}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/f53ca429503ba6a6ff69002cc63f9bf5.png)